MTE Relay Server On-Premise Deployment
Introduction
MTE Relay Server is an end-to-end encryption system that protects all network requests with next-generation application data security. It acts as a proxy server in front of your backend, communicating with an MTE Relay Client to encode and decode all network traffic. The server is highly customizable and supports integration with other services through custom adapters.
Below is a typical architecture where a client application communicates with an MTE Relay Server, which then proxies decoded traffic to backend services:
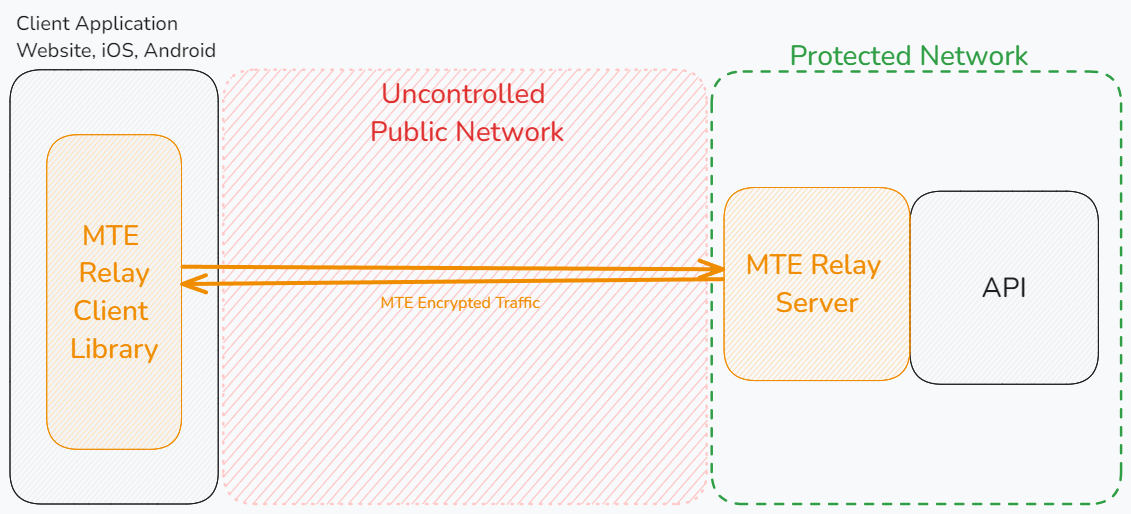
MTE Relay Servers can only communicate with MTE Relay Clients. An MTE API Relay cannot communicate with an MTE Relay Server or an MTE Relay Client SDK. MTE Relay Servers are strictly for client-to-server communications.
Prerequisites
Technical Requirements
- A web or mobile application project that communicates with a backend API over HTTP.
- Our demo app is available on GitHub: MTE Relay Demos.
- Docker installed and running on your system.
- AWS CLI installed.
Skills and Knowledge
- Familiarity with Docker and/or Kubernetes.
- Basic knowledge of configuring containerized services.
Credentials
- An AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key provided by Eclypses to access the private container repository.
Deployment Options
MTE Relay Server is provided as a Docker image and can be deployed on-premise using:
- Docker Run
- Docker Compose
- Kubernetes
- Other container runtimes (e.g., Podman, Docker Swarm, K3s)
1. Configure AWS CLI Access
You must configure a new AWS CLI profile using the credentials provided by Eclypses.
aws configure --profile eclypses-customer-on-prem
When prompted:
- AWS Access Key ID: Enter the ID provided by Eclypses.
- AWS Secret Access Key: Enter the secret key provided.
- Default region name: us-east-1
- Default output format: json
2. Pull the Docker Image
Authenticate Docker with the Eclypses ECR repository:
- bash
- PowerShell
aws ecr get-login-password \
--region us-east-1 \
--profile eclypses-customer-on-prem \
| docker login --username AWS \
--password-stdin 321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
aws ecr get-login-password `
--region us-east-1 `
--profile eclypses-customer-on-prem `
| docker login --username AWS `
--password-stdin 321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Then pull the image:
docker pull 321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/customer/on-prem/mte-relay-server:4.5.0
Video Guide
Server Configuration
MTE Relay Server is configured using environment variables.
Using a DOMAIN_MAP (Recommended)
DOMAIN_MAP is a JSON object keyed by the Host header that arrives with each request.
The value for each key is a settings object that tells the proxy how to process the request.
Settings
| Field | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| upstream | string | Full URL (http://localhost:8080, https://api.internal) |
| pass_through_routes | string[] | Paths that use standard HTTP proxy, without MTE encryption |
| client_id_secret | string | Legacy shared secret used by some auth layers |
| cors_origins | string[] | List of allowed CORS origins for preflight requests |
| cors_methods | string[] | List of allowed CORS methods for preflight requests |
| headers | string | A JSON object of additional headers to add to proxied requests |
Examples
- Single Proxy: Requests with Host header
mte-api.company.comare decrypted and forwarded tohttp://internal-service. The/healthroute is proxied without MTE encoding/decoding.
{
"mte-api.company.com": {
"upstream": "http://internal-service",
"client_id_secret": "8KeJmtuKweUhymNJmGHvGMrJCUtHxhQG",
"pass_through_routes": ["/health"],
"cors_origins": ["https://app.company.com"],
}
}
- Multi-service proxy that handles:
- Incoming encoded requests for
billing.company.io, forwarding tohttp://billing-servicewith/readyand/liveroutes unencoded. - Request to
auth.company.io, forwarding tohttp://auth-servicewith/healthroute unencoded. - All other requests (any Host) are proxied to
http://default-backend:8080without encoding.
{
"billing.company.io": {
"upstream": "http://billing-service",
"pass_through_routes": ["/ready", "/live"],
"client_id_secret": "8KeJmtuKweUhymNJmGHvGMrJCUtHxhQG",
"cors_origins": ["https://app.company.com"],
},
"auth.company.io": {
"upstream": "http://auth-service:3000",
"pass_through_routes": ["/health"],
"client_id_secret": "heYBRbTr3QNBgQFV6x6YpfWqyEs2Tj8F",
"cors_origins": ["https://app.company.com"],
"cors_methods": ["GET", "POST", "OPTIONS"]
},
"*": {
"upstream": "http://default-backend:8080",
"client_id_secret": "PmNPtWJMzz46S9k8cY7du5Z6XYc9B5Ad",
"cors_origins": ["https://app.company.com", "http://localhost:3000"],
}
}
Export as one-line env var:
export DOMAIN_MAP='{ "billing.company.io": { "upstream": "http://billing-service", "pass_through_routes": ["/ready", "/live"], "client_id_secret": "8KeJmtuKweUhymNJmGHvGMrJCUtHxhQG" }, "auth.company.io": { "upstream": "http://auth-service", "pass_through_routes": ["/health"], "client_id_secret": "heYBRbTr3QNBgQFV6x6YpfWqyEs2Tj8F" }, "*": { "upstream": "http://default-backend:8080", "client_id_secret": "PmNPtWJMzz46S9k8cY7du5Z6XYc9B5Ad" } }'
Host header derivation
The Host header is taken directly from the authority component of the absolute URL used in the request.
For example, https://api.example.com/users/1 the authority is api.example.com (port 443 is implicit for HTTPS), so the Host header sent by the client is exactly:
Host: api.example.com
If the URL contains an explicit port (https://api.example.com:8443/users/1) the header becomes:
Host: api.example.com:8443
DOMAIN_MAP must therefore use the exact same string—domain only, or domain:port—to match the incoming Host header. Or, use a wildcard "*" to match any host.
Host Matching
MTE Relay Server performs an exact match against the Host header (case-insensitive).
If an exact match is not found, it checks for a wildcard ("*").
If no match is found, the request is rejected with 404.
Using individual Environment Variables (Legacy)
Using these environment variables will result in the MTE Relay Server being configured to only handle a single domain. This method is deprecated in favor of using the DOMAIN_MAP variable. If both are provided, DOMAIN_MAP will take precedence.
Example:
UPSTREAM- Upstream API or service URL.CLIENT_ID_SECRET- Secret for signing client IDs (minimum 32 characters).PASS_THROUGH_ROUTES- Comma-separated list of routes proxied without encoding/decoding.CORS_ORIGINS- Comma-separated list of allowed origins.CORS_METHODS- Comma-separated list of allowed methods. Default:GET, POST, PUT, DELETE.
UPSTREAM='https://api.my-company.com'
CLIENT_ID_SECRET='2DkV4DDabehO8cifDktdF9elKJL0CKrk'
PASS_THROUGH_ROUTES='/health,/version'
OUTBOUND_TOKEN='s3cr3tT0k3nV4lu3'
Additional Environment Variables
PORT- Default:8080.LOG_LEVEL- One of trace, debug, info, warning, error, panic, disabled. Default:info.
Deployment Steps
Option A: Docker Run
Using the docker run command, we can launch a single MTE Relay container locally for testing or local development purposes.
Copy the command below, modify the environment variable values, and run it in your terminal.
- bash
- PowerShell
docker run --rm -it \
--name mte-relay \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e DOMAIN_MAP='{ "relay.example.com": { "upstream": "__YOUR_UPSTREAM_URL__", "client_id_secret": "__YOUR_CLIENT_ID_SECRET__", "cors_origins": ["__YOUR_CORS_ORIGINS__"] } }' \
321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/customer/on-prem/mte-relay-server:4.5.0
docker run --rm -it `
--name mte-relay `
-p 8080:8080 `
-e DOMAIN_MAP='{ "relay.example.com": { "upstream": "__YOUR_UPSTREAM_URL__", "client_id_secret": "__YOUR_CLIENT_ID_SECRET__", "cors_origins": ["__YOUR_CORS_ORIGINS__"] } }' `
321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/customer/on-prem/mte-relay-server:4.5.0
Command Explanation:
docker run
Runs a container from the specified image.--rm
Automatically removes the container when it exits.-it
Allocates an interactive terminal (-ifor interactive input,-tfor pseudo-TTY).--name mte-relay
Assigns a custom name (mte-relay) to the container.-p 8080:8080
Maps host port8080to container port8080. You may change the host port if needed. Do not change the container port.-e DOMAIN_MAP='...'
Sets theDOMAIN_MAPenvironment variable as a JSON string mapping domains to their configuration (upstream URL, client ID secret, CORS origins, etc.).- The last line is the image to run.
Video Guide
Option B: Docker Compose
Docker Compose provides a convenient way to define and manage multi-container applications by allowing you to describe all of your services in a single YAML file. Once defined, Docker Compose can automatically create and start the containers with a single command, ensuring consistency across environments.
Create a new file named docker-compose.yaml with the following content, and update the environment variable values as needed:
services:
mte-relay-server:
image: 321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/customer/on-prem/mte-relay-server:4.5.0
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- DOMAIN_MAP={ "relay.example.com": { "upstream": "__YOUR_UPSTREAM_URL__", "client_id_secret": "__YOUR_CLIENT_ID_SECRET__", "cors_origins": ["__YOUR_CORS_ORIGINS__"] } } # Update this value!
- REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379
depends_on:
- redis
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
Docker Compose Commands
To start the services defined in the docker-compose.yaml file, run:
docker compose up
Helpful CLI Flags:
-f- Specify an alternate compose file.- Example:
docker compose -f custom.yml up
- Example:
-d- Run containers in the background.- Example:
docker compose up -d
- Example:
Check running containers with:
docker compose ps
Stop the services with:
docker compose down
In production environments, it may be better to use a Docker Swarm cluster for improved scalability, isolation of services, rolling updates, and management.
Sources:
Docker Compose Documentation
Docker Compose CLI
Video Guide
Option C: Kubernetes
Kubernetes provides a powerful system for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. By defining resources in YAML files, it ensures reliability, scalability, and consistency across environments.
Create a file named mte-relay-deployment.yaml with the following content:
# MTE Relay container deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mte-relay-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mte-relay
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mte-relay
spec:
containers:
- name: mte-relay-server
image: 321186633847.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/customer/on-prem/mte-relay-server:4.5.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: DOMAIN_MAP
value: '{ "relay.example.com": { "upstream": "__YOUR_UPSTREAM_URL__", "client_id_secret": "__YOUR_CLIENT_ID_SECRET__", "cors_origins": ["__YOUR_CORS_ORIGINS__"] } }' # Update this value!
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis://my-redis-service:6379"
Video Guide
MTE Relay Service to expose the deployment
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mte-relay-service spec: type: LoadBalancer selector: app: mte-relay ports:
- protocol: TCP port: 8080 # External port, you may change this if needed targetPort: 8080
Redis container deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: my-redis-deployment spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: my-redis template: metadata: labels: app: my-redis spec: containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:7.2
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
Redis Service to expose the deployment
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: my-redis-service spec: type: ClusterIP selector: app: my-redis ports:
- protocol: TCP port: 6379 targetPort: 6379
The above configuration provides these resources:
- `mte-relay-deployment (Deployment)`: Runs 2 replicas of the mte-relay-server container, exposing port 8080 with environment variables for upstream service, client secret, CORS, and Redis connection.
- `mte-relay-service (Service - LoadBalancer)`: Exposes the mte-relay pods externally on port 80, forwarding traffic to container port 8080.
- `my-redis-deployment (Deployment)`: Runs a single Redis instance on port 6379.
- `my-redis-service (Service - ClusterIP)`: Provides internal cluster access to the Redis pod over port 6379.
#### Kubernetes Commands
To deploy the application to your kubernetes cluster, run:
```bash
kubectl apply -f mte-relay-deployment.yaml
You can check the status of your deployment with:
kubectl get deployments
kubectl get pods
kubectl get services
To check the logs of a running pod, use the command
kubectl logs <POD_NAME>
To scale up the number of replicas, use the command
kubectl scale deployment mte-relay-deployment --replicas=<NUMBER_OF_REPLICAS>
To delete the deployment and service, use the command
kubectl delete -f mte-relay-deployment.yaml
Source: Kubernetes Deployments
Testing & Health Checks
- Monitor container logs for startup messages
- Use the default or custom echo routes to test container responsiveness:
- Default:
/api/mte-echo - Custom Message:
/api/mte-echo?msg=test
- Default:
Expected response:
{
"message": "test",
"timestamp": "<timestamp>"
}
Troubleshooting
- Invalid Configuration
- Check logs for missing/invalid environment variables.
- Relay unreachable
- Verify firewall, networking, or Kubernetes service configuration.
- Redis connection issues
- Ensure
REDIS_URLis reachable in your environment.
- Ensure
Security
- No sensitive data stored in the container.
- No root privileges required.
Costs
Private infrastructure costs (VMs, storage, networking, Redis clusters) are customer-managed.
Maintenance
Routine Updates
- Updated container images are distributed through Eclypses.
Fault Recovery
- Relaunch the Relay container; clients will automatically re-pair.
Support
For assistance, contact Eclypses Support:
📧 customer_support@eclypses.com
🕒 Monday–Friday, 8:00 AM–5:00 PM MST (excluding holidays)